이 문서의 내용
이 프로젝트의 개발 환경
- 개발 언어 및 주요 환경
- Visual Studio 2022
- C++ 17
- 기타 환경
- Boost 1.84.0
부스트(Boost) 라이브러리
부스트(Boost)는 C++ 표준 라이브러리와 함께 사용 할 수 있는 무료 라이브러리입니다.
Linux Unix Windows를 포함한 대부분의 OS에서 실행되며 JSON 알고리즘 파일 시스템 스마트 포인터 등 확장 함수를 제공합니다.
| JSON | 알고리즘 | 파일 시스템 | 스마트 포인터 |
| JSON 형식의 파일을 읽고 파싱하기 위한 함수를 제공합니다. | 정렬, 검색, 난수 생성과 같은 작업을 위한 알고리즘을 제공합니다. | 파일 및 디렉토리에 대한 접근과 제어를 위한 함수를 제공합니다. | auto_ptr, shared_ptr, weak_ptr 등에 대한 스마트 포인터를 제공합니다. |
부스트 설치
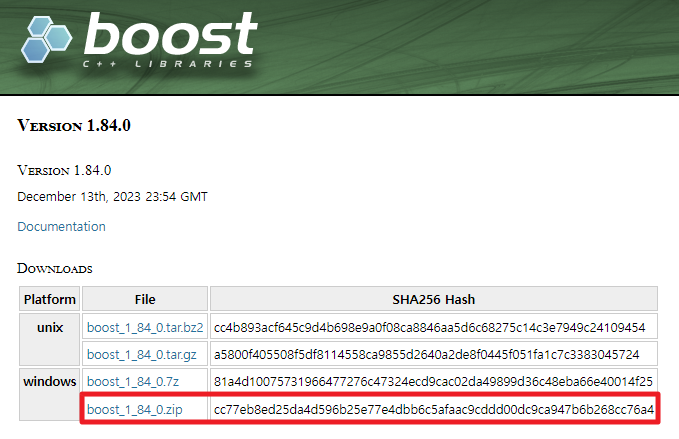
부스트(Boost)에서 최신 버전의 Windows 부스트 파일(zip)을 다운로드합니다.
다운로드 파일의 압축을 해제하고 boostrap.bat 파일을 실행합니다.
$ boostrap.bat
2024-02-21 오후 08:51 253,440 b2.exe
1개 파일 253,440 바이트
0개 디렉터리 5,218,021,376 바이트 남음
Generating Boost.Build configuration in project-config.jam for msvc...
Bootstrapping is done. To build, run:
.\b2
To adjust configuration, edit 'project-config.jam'.
Further information:
- Command line help:
.\b2 --help
- Getting started guide:
http://boost.org/more/getting_started/windows.html
- Boost.Build documentation:
http://www.boost.org/build/설치 후 b2 --help를 사용하여 메뉴얼을 표시 할 수도 있습니다.
$ b2 --help
B2 4.10-git
Project-specific help:
Project has jamfile at Jamroot
Usage:
b2 [options] [properties] [install|stage]
Builds and installs Boost.
Targets and Related Options:
install Install headers and compiled library files to the
======= configured locations (below).
--prefix=<PREFIX> Install architecture independent files here.
Default: C:\Boost on Windows
Default: /usr/local on Unix, Linux, etc.
--exec-prefix=<EPREFIX> Install architecture dependent files here.
Default: <PREFIX>
--libdir=<LIBDIR> Install library files here.
Default: <EPREFIX>/lib
--includedir=<HDRDIR> Install header files here.
Default: <PREFIX>/include
--cmakedir=<CMAKEDIR> Install CMake configuration files here.
Default: <LIBDIR>/cmake
--no-cmake-config Do not install CMake configuration files.
stage Build and install only compiled library files to the
===== stage directory.
--stagedir=<STAGEDIR> Install library files here
Default: ./stage
Other Options:
--build-type=<type> Build the specified pre-defined set of variations of
the libraries. Note, that which variants get built
depends on what each library supports.
-- minimal -- (default) Builds a minimal set of
variants. On Windows, these are static
multithreaded libraries in debug and release
modes, using shared runtime. On Linux, these are
static and shared multithreaded libraries in
release mode.
-- complete -- Build all possible variations.
--build-dir=DIR Build in this location instead of building within
the distribution tree. Recommended!
--show-libraries Display the list of Boost libraries that require
build and installation steps, and then exit.
--layout=<layout> Determine whether to choose library names and header
locations such that multiple versions of Boost or
multiple compilers can be used on the same system.
-- versioned -- Names of boost binaries include
the Boost version number, name and version of
the compiler and encoded build properties. Boost
headers are installed in a subdirectory of
<HDRDIR> whose name contains the Boost version
number.
-- tagged -- Names of boost binaries include the
encoded build properties such as variant and
threading, but do not including compiler name
and version, or Boost version. This option is
useful if you build several variants of Boost,
using the same compiler.
-- system -- Binaries names do not include the
Boost version number or the name and version
number of the compiler. Boost headers are
installed directly into <HDRDIR>. This option is
intended for system integrators building
distribution packages.
The default value is 'versioned' on Windows, and
'system' on Unix.
--buildid=ID Add the specified ID to the name of built libraries.
The default is to not add anything.
--python-buildid=ID Add the specified ID to the name of built libraries
that depend on Python. The default is to not add
anything. This ID is added in addition to --buildid.
--help This message.
--with-<library> Build and install the specified <library>. If this
option is used, only libraries specified using this
option will be built.
--without-<library> Do not build, stage, or install the specified
<library>. By default, all libraries are built.
Properties:
toolset=toolset Indicate the toolset to build with.
variant=debug|release Select the build variant
link=static|shared Whether to build static or shared libraries
threading=single|multi Whether to build single or multithreaded binaries
runtime-link=static|shared
Whether to link to static or shared C and C++
runtime.
General command line usage:
b2 [options] [properties] [targets]
Options, properties and targets can be specified in any order.
Important Options:
* --clean Remove targets instead of building
* -a Rebuild everything
* -n Don't execute the commands, only print them
* -d+2 Show commands as they are executed
* -d0 Suppress all informational messages
* -q Stop at first error
* --reconfigure Rerun all configuration checks
* --durations[=N] Report top N targets by execution time
* --debug-configuration Diagnose configuration
* --debug-building Report which targets are built with what properties
* --debug-generator Diagnose generator search/execution
Further Help:
The following options can be used to obtain additional documentation.
* --help-options Print more obscure command line options.
* --help-internal B2 implementation details.
* --help-doc-options Implementation details doc formatting.
...found 1 target...msvc로 부스트 빌드
부스트를 프로젝트에 포함시키려면 msvc를 사용하여 빌드합니다.
mvsc 버전 확인하려면 Visual Studio를 실행 후 다음 소스 코드를 작성하고 실행합니다.
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << _MSC_VER << std::endl;
}이 프로젝트의 msvc 버전은 1939이며 Visual Studio 버전은 Visual Studio 2022 버전 17.10입니다.
msvc 버전과 Visual Studio 버전 매핑은 Microsoft documents: compiler-version(msvc-170)을 참고합니다.
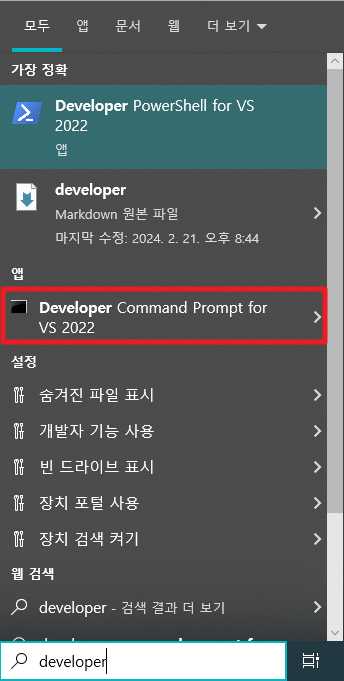
VS 버전과 일치하는 Developer Command Prompt를 실행합니다.
프롬프트가 실행되면 부스트 압축 해제 경로에서 msvc 버전을 사용해 부스트를 빌드합니다.
$ b2 toolset=msvc-17.9 variant=debug,release link=static threading=multi address-model=64 runtime-link=static| 코드 | 비고 | |
| msvc 버전을 입력합니다. | ||
| debug 및 release 환경으로 빌드합니다. | ||
| static 라이브러리로 빌드합니다. | ||
| 멀티스레드 바이너리로 빌드합니다. | ||
| 64비트 환경으로 빌드합니다. 32비트 환경에서 빌드하려면 32를 입력합니다. | ||
| static C++ 런타림 라이브러리로 빌드합니다. | ||
$ cd <부스트 압축 해제 경로>
$ b2 toolset=msvc-17.9 variant=debug,release link=static threading=multi address-model=64 runtime-link=static
...
The Boost C++ Libraries were successfully built!
The following directory should be added to compiler include paths:
C:\Users\namep\Downloads\boost_1_84_0\boost_1_84_0
The following directory should be added to linker library paths:
C:\Users\namep\Downloads\boost_1_84_0\boost_1_84_0\stage\lib| 코드 | 비고 | |
부스트 라이브러리를 프로젝트에 포함
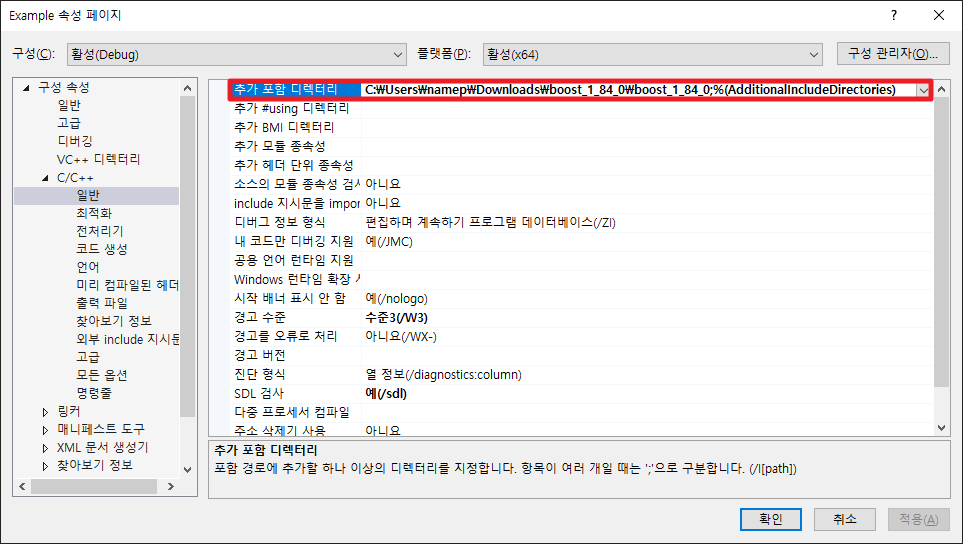
프로젝트 | 속성 | 구성 속성 | C/C++ | 일반 탭에서 추가 포함 디렉토리에 compiler inlude 경로를 추가합니다.
프로젝트 | 속성 | 구성 속성 | 링커 | 일반 탭에서 추가 라이브러리 디렉토리에 linker library 경로를 추가합니다.
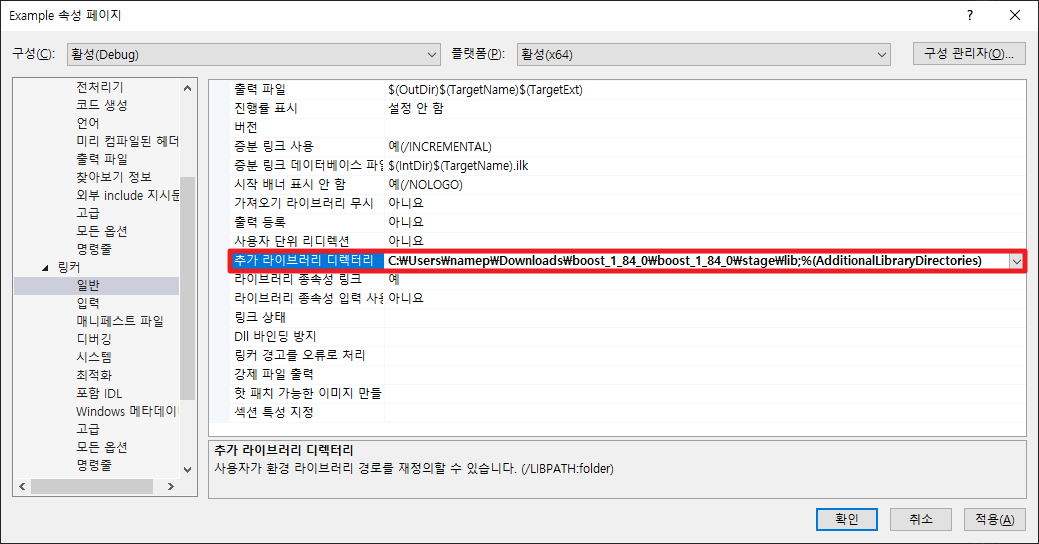
소스 파일을 생성하고 다음을 작성합니다.
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/random.hpp>
int main()
{
boost::mt19937 gen;
boost::uniform_int<> dest(-100, 100);
boost::variate_generator<boost::mt19937, boost::uniform_int<>> rand(gen, dest);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
std::cout << i << " : " << rand() << std::endl;
}애플리케이션을 실행하고 결과를 확인합니다.
0 : 63
1 : -73
2 : 82
3 : 67
4 : -75
5 : 94
6 : 83
7 : -56
8 : 27
9 : -39
10 : -81
11 : 9
12 : -45
13 : -63
14 : 9
15 : 99
16 : 92
17 : 100
18 : 93
19 : 94'C++ > Libraries, Plugins, 3rd-Party' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (Redis) hiredis를 사용한 C++ 프로젝트와 Redis 서버 연동 (0) | 2024.02.19 |
|---|

